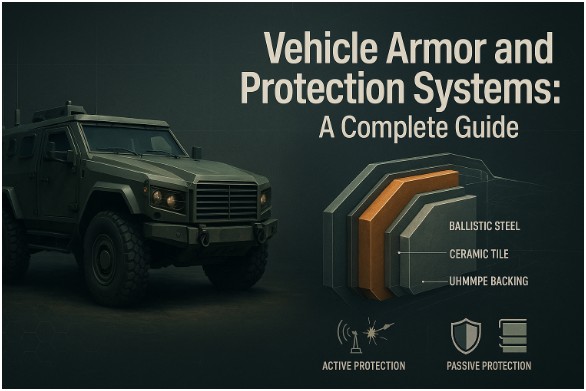
Vehicle armor has advanced from basic steel plating to sophisticated multi-layered systems that protect against threats like small arms fire and rocket-propelled grenades.
Used by military contractors, law enforcement, and security-conscious civilians, modern protection includes technologies like ballistic steel and reactive armor to ensure safety and prevent failure.
The Evolution of Vehicle Armor Through History
Vehicle armor began during World War I when armies first mounted steel plates on trucks and early tanks. These rudimentary solutions offered basic protection but came with severe weight penalties that limited mobility and fuel efficiency.
World War II marked a turning point in armor development. German engineers pioneered sloped armor designs that deflected projectiles more effectively than vertical plates.
Meanwhile, Allied forces developed composite armor systems combining steel with other materials to improve protection without excessive weight increases.
The Cold War era introduced reactive armor—explosive tiles that detonate outward when struck, disrupting incoming projectiles before they could penetrate the main armor. This technology revolutionized tank protection and remains a cornerstone of modern armored vehicle design.
Recent decades have seen armor technology accelerate rapidly. Computer modeling now allows engineers to optimize protection systems before physical testing, while new materials like ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene offer impressive ballistic resistance at a fraction of steel’s weight.
Modern Armor Materials: Beyond Steel
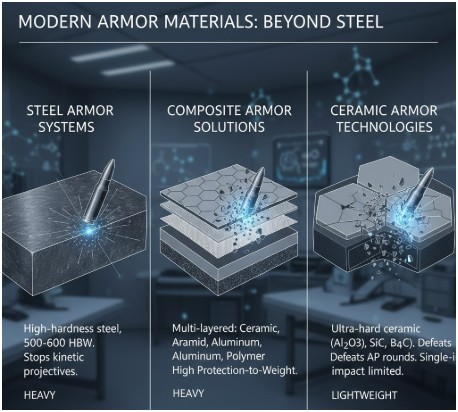
Steel Armor Systems
Traditional ballistic steel remains the backbone of most armored vehicles. Modern steel armor uses specialized alloys hardened through precise heat treatment processes. These steels can stop rifle rounds and shrapnel while maintaining structural integrity under repeated impacts.
High-hardness armor steel typically measures between 500-600 HBW (Brinell hardness), providing excellent protection against kinetic energy projectiles. However, steel’s weight limitations make it less suitable for lighter vehicles requiring enhanced mobility.
Composite Armor Solutions
Composite armor combines multiple materials to achieve superior protection-to-weight ratios. Typical composite systems layer steel, aluminum, ceramics, and polymer materials in carefully engineered configurations.
These systems work by disrupting projectile energy through multiple mechanisms. Ceramic layers shatter incoming projectiles, while backing materials absorb remaining energy. The result is protection levels that would require much thicker steel armor alone.
Ceramic Armor Technologies
Ceramic armor represents the cutting edge of lightweight protection. Materials like aluminum oxide, silicon carbide, and boron carbide offer exceptional hardness that can defeat armor-piercing rounds.
When a projectile strikes ceramic armor, the ceramic fractures in a controlled manner that breaks up the projectile while distributing impact energy across a larger area. Backing materials then catch fragments and absorb remaining kinetic energy.
The main limitation of ceramic armor is its vulnerability to multiple impacts in the same area. Once ceramic tiles fracture, their protective capability degrades significantly, requiring replacement after combat exposure.
Active vs. Passive Protection Systems
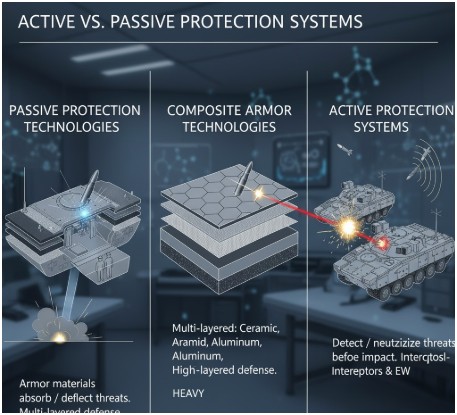
Passive Protection Technologies
Passive protection relies on armor materials and design to absorb or deflect threats. This includes traditional armor plating, spall liners that catch interior fragments, and blast-resistant flooring that redirects explosion energy away from occupants.
Modern passive systems often incorporate multiple protection layers. External armor stops initial penetration attempts, while internal systems protect against fragments and overpressure effects. This steady rest approach to layered defense ensures comprehensive protection against diverse threats.
Active Protection Systems
Active protection systems detect incoming threats and deploy countermeasures to neutralize them before impact. These systems use radar or other sensors to track approaching projectiles, then fire interceptors or deploy electronic countermeasures.
Israeli Trophy systems exemplify active protection technology. When Trophy detects an incoming rocket or missile, it fires a shotgun-like interceptor that destroys the threat several meters from the protected vehicle. This prevents damage to the armor and eliminates blast effects on nearby personnel.
Electronic warfare systems represent another active protection category. These systems jam guided weapons or spoof their guidance systems, causing them to miss their targets entirely.
Military Applications and Requirements
Military armored vehicles face the most demanding protection requirements. Main battle tanks must withstand direct hits from tank guns and anti-tank missiles while maintaining combat effectiveness. Infantry fighting vehicles need protection against small arms and artillery fragments while preserving mobility for rapid deployment.
Modern military armor systems often feature modular designs allowing protection levels to be adjusted based on threat environments. Base armor provides protection against standard threats, while add-on modules can be installed for high-risk missions requiring enhanced protection.
Weight distribution becomes critical in military applications. Armor must protect vital areas while maintaining vehicle balance and mobility. Computer modeling helps engineers optimize armor placement to maximize protection efficiency without compromising vehicle performance.
Civilian and Commercial Applications

Civilian armored vehicles serve executives, diplomats, and high-risk personnel in dangerous environments. These vehicles prioritize discretion over maximum protection, using armor systems that maintain normal vehicle appearance while providing significant ballistic protection.
B6 and B7 armor standards define civilian protection levels against handguns and rifles respectively. Civilian armor systems often emphasize glass protection, as windows represent the most vulnerable areas in passenger vehicles.
Commercial armored vehicles include cash transport trucks and security vehicles. These applications balance protection requirements with operational costs, typically using steel armor systems that provide reliable protection at reasonable prices.
Legal and Regulatory Framework
Armor system regulations vary significantly between countries and applications. Military armor faces strict export controls, while civilian armor may be restricted or prohibited in certain jurisdictions.
International Traffic in Arms Regulations (ITAR) controls military armor technology exports from the United States. These regulations ensure that advanced protection technologies don’t fall into unauthorized hands while allowing legitimate defense cooperation between allied nations.
Civilian armor regulations focus primarily on ensuring that armored vehicles don’t pose public safety risks. Vehicle weight limits, crash safety standards, and equipment specifications must be met before armored vehicles can operate on public roads.
The Future of Vehicle Protection
Emerging technologies promise revolutionary advances in vehicle protection. Electromagnetic armor systems could use electric fields to deflect metallic projectiles, while smart materials might change properties instantly in response to threats.
Artificial intelligence integration will enhance active protection systems, allowing faster threat identification and response. Machine learning algorithms could predict attack patterns and pre-position countermeasures for maximum effectiveness.
Nanotechnology offers possibilities for ultra-lightweight armor materials with properties surpassing current ceramic systems. These materials could provide tank-level protection at the weight of traditional steel armor.
Conclusion
Now that we have explored the various technologies that can be integrated into military systems, it is clear that the future of warfare will rely heavily on advanced technology.
From autonomous vehicles to artificial intelligence and nanotechnology, these advancements will significantly enhance our military capabilities and provide a significant advantage on the battlefield.